To avoid needing to use webpack, npm or any other build tooling, Vue components are written in TypeScript Class-Style Vue Components utilizing annotations in vue-class-component & vue-property-decorator, e.g. here's Blazor WASM Counter Page:
@page "/counter"
<h1>Counter</h1>
<p>Current count: @currentCount</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" @onclick="IncrementCount">Click me</button>
@code {
private int currentCount = 0;
private void IncrementCount()
{
currentCount++;
}
}
Written as a TypeScript Class-Style Vue Component:
@Component({ template:`
<div>
<h1>Counter</h1>
<p>Current count: {{currentCount}}</p>
<button class="btn btn-primary" @click="incrementCount()">Click me</button>
</div>`})
export class Counter extends Vue {
currentCount = 0;
incrementCount() {
this.currentCount++;
}
}
INFO
Vue's integration with TypeScript is set to improve in Vue 3 which will be written in TypeScript
Typed DTOs
The typing benefits of C# is also available when using TypeScript with type definitions available for all libraries which provides rich intelli-sense & type checking during development.
Thanks to ServiceStack's Add TypeScript Reference feature, Types are also available for your C# Services which can be updated by running npm run dtos or app ts directly, e.g:
$ app ts
Which will update all dtos.ts TypeScript Reference DTOs with the latest changes which can be used together with the @servicestack/client generic Service Client to provide both a terse & typed API for consuming back-end end-to-end Typed C# APIs:
import { Hello } from "../shared/dtos";
import { client } from "../shared";
@Component({ template:`
<div>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
Welcome to your new app.
<div class="row mt-4 p-0">
<div class="col col-3">
<v-input placeholder="Your name" v-model="txtName" />
</div>
<h3 class="col col-5 result mt-2">{{ result }}</h3>
</div>
</div>`})
export class Home extends Vue {
public txtName: string = '';
public result: string = '';
@Watch('txtName')
async onNameChanged(value: string, oldValue: string) {
await this.nameChanged(value);
}
async nameChanged(name: string) {
if (name) {
const r = await client.get(new Hello({ name }));
this.result = r.result;
} else {
this.result = '';
}
}
}
AutoQuery Services
Another major productivity boost for rapidly developing data-driven APIs is AutoQuery RDBMS where you can simply create queryable APIs by just declaratively defining which fields you want to query using any of the registered conventions, e.g:
[Route("/forecasts")]
[Route("/forecasts/{Id}")]
public class QueryWeatherForecasts : QueryDb<WeatherForecast>
{
public int? Id { get; set; }
public DateTime? BeforeDate { get; set; }
public DateTime? AfterDate { get; set; }
public int? BelowTemperatureC { get; set; }
public int? AboveTemperatureC { get; set; }
}
public class WeatherForecast
{
[AutoIncrement]
public int Id { get; set; }
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public string Summary { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
}
Which is all that's required for ServiceStack to automatically implement the Service where it has access to all standard Typed API metadata services like being included in the generated TypeScript client DTOs:
$ npm run dtos
Which FetchData.ts uses to power its dynamic Queryable UI by sending a populated QueryWeatherForecasts Request DTO configured with any filters and re-executed on every input change:
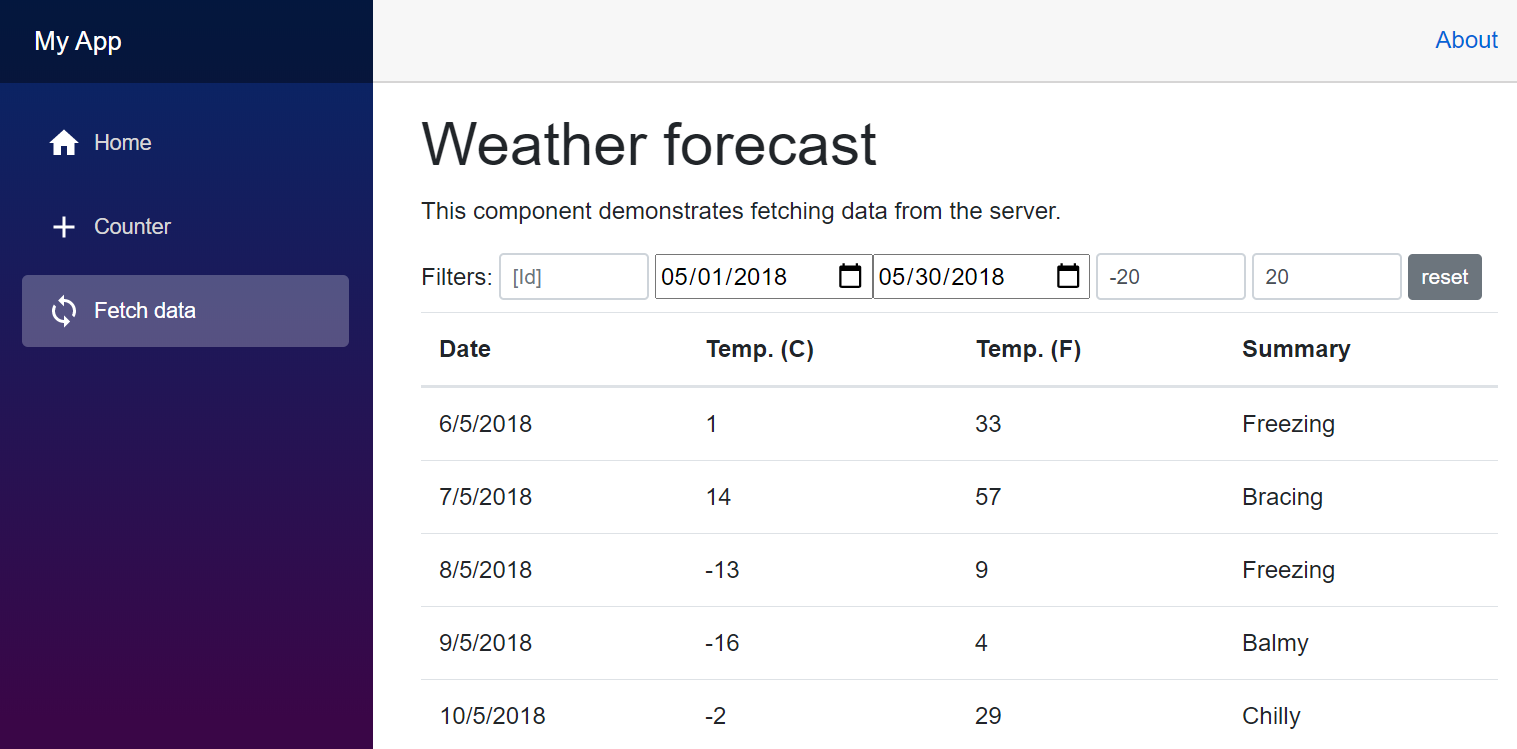
<form class="form-inline mb-2" @submit.prevent="">
<label for="txtId">Filters: </label>
<input class="form-control form-control-sm mx-1" type="number" placeholder="[Id]" v-model="id" @input="filter">
<input type="date" v-model="afterDate" @change="filter">
<input type="date" v-model="beforeDate" @change="filter">
<input class="form-control form-control-sm mx-1" type="number" placeholder="Above (C)" v-model="aboveTemp" @input="filter">
<input class="form-control form-control-sm mr-1" type="number" placeholder="Below (C)" v-model="belowTemp" @input="filter">
<button class="btn btn-secondary btn-sm" @click="reset">reset</button>
</form>
Triggering a call to filter() to populate and resend the QueryWeatherForecasts Request DTO with the latest filters and update the forecasts Reactive UI Model:
export class FetchData extends Vue {
forecasts:WeatherForecast[]|null = null;
id = '';
beforeDate = '';
afterDate = '';
belowTemp = '';
aboveTemp = '';
async filter() {
const request = new QueryWeatherForecasts();
if (this.id) request.id = parseInt(this.id);
if (this.beforeDate) request.beforeDate = this.beforeDate;
if (this.afterDate) request.afterDate = this.afterDate;
if (this.belowTemp) request.belowTemperatureC = parseInt(this.belowTemp);
if (this.aboveTemp) request.aboveTemperatureC = parseInt(this.aboveTemp);
this.forecasts = (await client.get(request)).results;
}
}